NanoLocz
NanoLocz User Guide 
Installation - - Getting Started - - Saving Data
Level - -
Detect - -
FineAlign - -
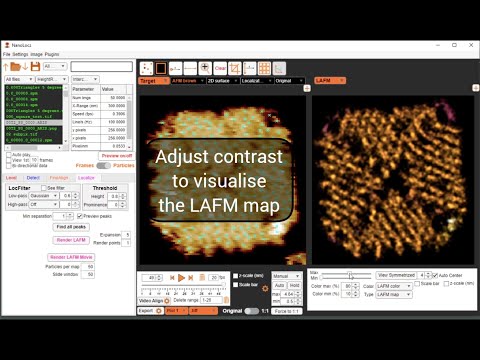
Localize
Area Analysis - - Keyboard Shortcuts
Simulation AFM - - YouTube Video Tutorials
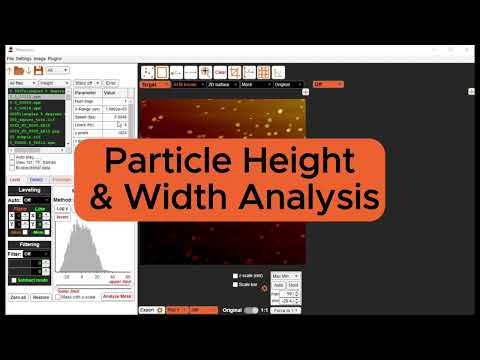
Particle Detection
Two methods are implemented for particle detection using either template matching image correlation to a reference image (ROI method) or local maxima (peak method). Once particles have been detected particle tracking can be run on their coordinates.
1. ROI Method
2. Peak Method
3. Particle Tracking
4. YouTube Videos on Particle Analysis
1. ROI Method
The ROI (region of interest) method uses image cross-correlation of a reference image with the full image or video data set to detect particles with high correlation.
- After levelling your image/movie select the detect tab
- Select ROI as the detection method
- Select a reference image using either of the following methods:
Manual selection: Select any of the Orange Square icons and then manually draw a square around a representative particle in your AFM data.
Simulated Selection: Open Simulation AFM by selecting Tools -> Simulation AFM. Import the pdb of the expected structure. Orientate the molecule and alter the tip radius to match the expected orientation and tip size in the AFM images. Select ‘Export to NanoLocz’. More info on Simulation AFM. - Select Find Particles.
- Particle detections can be viewed using the Overlay Plot options.
- If too many particles have been picked - use the lower limit slider in the Filter detections histogram to selectively exclude particles with lower correlation to the reference image.
Detection Options:
- Exclude Edges: Exclude picking features at the edge of images.\
- Fast find: Images are down sampled by x2 to increase picking speed. Not recommended for reference images with low pixel count.\
- Filter xcor image: Apply a Gaussian filter to the cross-correlation image to reduce over picking/\
- Filter image: Apply a Gaussian filter to the image to reduce over picking (filtered image is only used for detection and does not change the data).
Reference Tab Options:
- Allow rotation: To detect different rotations of a particle the detection can be run with rotation enabled, in this mode the cross-correlation is run with different rotations of the reference image to different angles. Enter the values as (starting angle):(interval):(final angle), for example -20:10:20 will perform detection at -20, -10, 0, 10 and 20 degrees reference rotation. Angles be further refined after defection using FineAlign.
- Centre Reference: Centre the reference image based on symmetry. If symmetry = 1 centring will be performed using the centre of mass.
- Average Reference: Take the image average of all included detections. If required this average image can be then used as a new reference image to refine the particle detection.
- Rotational Avg: Take rotational average image based on the user defined symmetry value.
2. Peak Method
The peak method of particle detection find local maxima above the Min Height threshold within neighborhood of pixel distances set by Min Separation.
- After levelling your image/movie select the detect tab
- Select Peaks as the detection method.
- Set the Min Height value above the background height.
- Set the ** Filter image** value to Gaussian filter to the image to reduce over picking (filtered image is only used for detection and does not change the data).
- Set Min Separation to reduce picking of multiple peaks on the same particle.
- Preview peaks to visualize the current detection settings.
- If needed particles are extracted from the images based on a user defined box size
- Auto Profile Option: turn on to automatically line profile all detected particles to calculate particle widths and heights in the horizontal, vertical and diagonal directions. Set Line length in units of pixels to a length which fully contours the particle.
- Select Find Particles.
- Go to Tools -> Plotter to visualize and access particle detection data.
3. Particle Tracking
- After particle have been detected, select the Run Tracking button
Tracking Options:
Max step: Maximum step distance a particle can be tracked (in pixels) between frames.
Max missing: Maximum number of frame particle can go missing for and still be tracked as the same particle.
Particle coordinates are input into the simpletracker algorithm (https://github.com/tinevez/simpletracker) to track particle positions over time. In brief particle pairs identified between frames as the closest (based on Euclidean distance) are connected to form links. Using the Hungarian algorithm the sum of these pair distances is minimized across all particles between successive frames. Subsequently, a second iteration examined track endings. If a track’s start closely aligned with another track’s end in the subsequent frames, a link spanning multiple frames is established, effectively bridging the gap and reestablishing the track. The method allows tracking to bridge a user defined number of frames where a particle is missing/undetected.